Photorefractive Effect
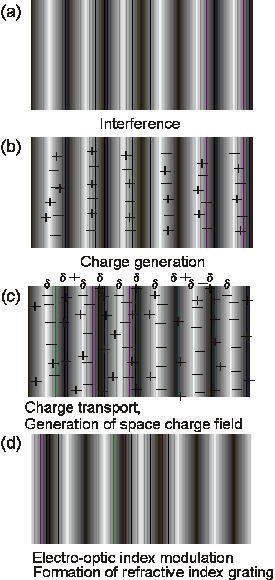
The photorefractive effect is a phenomenon in which a change in the refractive index of a material is induced by the absorption of light. The change in refractive index through the photorefractive effect occurs only within the interference fringe of the incident laser beams. When laser beams interfere in a photorefractive material, charge separation occurs between the light and the dark positions of the interference fringe. A space-charge field (internal electric field) is built at the area between the light and the dark positions. The refractive index of the corresponding area is changed through electrooptic effects. Thus, a refractive index grating is formed at the interference fringe. Dynamic volume holograms are easily formed through the photorefractive effect and this effect has direct applicability in photonics, including optical image processing, parallel optical logic, fringe recognition, and phase conjugation. The photorefractive effect was first observed in inorganic crystal lithium niobate in 1967 [1] and observed in an organic material in 1990.[2] Several reviews concerning the development of photorefractive materials have been published.[3-7] The photorefractive effect of organic materials, such as glassy polymers,[8-23] low-molecular-weight nematic liquid crystals,[24-28] liquid crystalline polymers,[29-35] ferroelectric liquid crystals,[36-42] polymer/liquid crystal composites[43-55] and amorphous compounds[56,57], have been reported since 1990 and extremely high photorefractivity has been achieved in organic polymer materials. The high photorefractivity of polymer materials arises from a change in chromophoric orientation induced by the internal electric field, termed orientational enhancement.[4,15,17] The photorefractive efficiency of organic materials is several times that of inorganic photonic crystals, and the organic polymers can easily be processed into films and also into fibers. This is advantageous for photonic applications.
Rerferences
| 1. | F. S. Chen, J. Appl. Phys., 38, 3418 (1967). |
| 2. | K. Shutter, J. Hulliger, P. Gunter, Solid State Commun., 74, 867 (1990). |
| 3. | L. Solymar, J. D. Webb, A. Grunnet-Jepsen, "The Physics and Applications of Photorefractive Materials", Oxford, New York, 1996. |
| 4. | P. Yeh, "Introduction to Photorefractive Nonlinear Optics", John Wiley, New York, 1993. |
| 5. | W. E. Moerner, S. M. Silence, Chem. Rev., 94, 127 (1994). |
| 6. | B. Kippelen, N. Peyghambarian, "Advances in Polymer Science, Polymers for Photonics Applications II", Springer, 2002. |
| 7. | O. Ostroverkhova, W. E. Moerner, Chem. Rev., 104, 3267 (2004). |
| 8. | Y. Zhang, Y. Cui, P. N. Preasad, Phys. Rev. B, 46, 9900 (1992). |
| 9. | B. Kippelen, Sandalphon, N. Peyghambarian, S. R. Lyon, A. B. Padias, H. K. Hall Jr, Electron Lett. 29, 1873 (1993). |
| 10. | W.-K. Chan, Y. Chen, Z. Peng, L. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 115, 11735 (1993) |
| 11. | Z. Peng, Z. Bao, L. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 116, 6003 (1994) |
| 12. | K. Meerholz, B. L. Volodin, B. Kippelen, N. Peyghambarian, Nature, 371, 497 (1994). |
| 13. | B. L.Volodin, B. Kippelen, K. Meerholz, B. Javidi, N. Peyghambarian, Nature, 383, 58 (1996) |
| 14. | Z. Peng, A. R. Gharavi, L. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 119, 4622 (1997) |
| 15. | Y. Cui, B. Swedek, N. Cheng, K. S. Kim, P.N. Prasad, J. Phys. Chem. B, 101, 3530 (1997) |
| 16. | A. Grunnet-Jepsen, C. L. Thompson, W. E. Moerner, Science, 277, 549 (1997) |
| 17. | B. Kippelen, S. R. Marder, E. Hendrickx, J.L. Maldonado, G. Guillemet, B.L. Volodin, D.D. Steele, Y. Enami, Sandalphon, Y. J. Yao, J.F. Wang, H. R?ckel, L. Erskine, N. Peyghambarian, Science, 279, 54 (1998) |
| 18. | K. Meerholz, Y.D. Nardin, R. Bittner, R. Wortmann, F. W?rthner, Appl. Phys. Lett., 73, 4 (1998) |
| 19. | E. Hendrickx, J.F. Wang, J.L. Maldonado, B.L. Volodin, E.A. Mash, A. Persoons, B. Kippelen, N. Peyghambarian, Macromolecules, 31, 734 (1998) |
| 20. | E. Hattemer, R. Zentel, E. Mecher, K. Meerholz, Macromolecules 33, 1972 (2000). |
| 21. | D.V. Steenwinckel, C. Engels, E. Gubbelmans, E. Hendrikx, C. Samyn, A. Persoons, Macromolecules, 33, 4074 (2000) |
| 22. | L. Yu, J. Poly. Sci. A, 39, 2557 (2001) |
| 23. | D. Wright, U. Gubler, W. E. Moerner, M. S. CeClue, J. S. Siegel, J. Phys. Chem. B, 107, 4732 (2003). |
| 24. | L. C. Khoo, H. Li, Y. Liang, Opt. Lett., 19, 1723 (1994). |
| 25. | I. C. Khoo, "Liquid Crystals: Physical Properties and Nonlinear Optical Phenomena", Wiley, New York, 1995. |
| 26. | G. P. Wiederrecht, B. A. Yoon M. R. Wasielewski, Science, 270, 1794 (1995). |
| 27. | G. P. Wiederrecht, B. Yoon, W. A. Svec, Wasielewski, M. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 119, 3358 (1997). |
| 28. | G. P. Wiederrecht, M. R. Waiselewski, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 120, 3231 (1998). |
| 29. | T. Sasaki, S. Hamada, Y. Ishikawa, T. Yoshimi, Chem. Lett., 1183 (1997). |
| 30. | T. Sasaki, M. Goto, Y. Ishikawa, T. Yoshimi, J. Phys. Chem.B, 103, 1925 (1999). |
| 31. | T. Sasaki, Proc. SPIE, 3799, 14, (1999). |
| 32. | T. Sasaki, K. Tachibana, K. Ohno, T. Shimada, M. Kudo, A. Katsuragi, T. Furuta, Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst., 368, 345, (2001). |
| 33. | T. Sasaki, T. Shimada, K. Tachibana, Chem. Lett., 324 (2002). |
| 34. | T. Sasaki, R. Kai, A. Sato, Y. Ishikawa, T. Yoshimi, Mol. Cryat. Liq. Cryst., 373, 53 (2002). |
| 35. | T. Sasaki, G. Fukunaga, Chem. Mater., 17, 3433 (2005). |
| 36. | T. Sasaki, Y. Kino, M. Shibata, N. Mizusaki, A. Katsuragi, Y. Ishikawa, T. Yoshimi, Appl. Phys. Lett., 78, 4112 (2001). |
| 37. | T. Sasaki, A. Katsuragi, K. Ohno, J. Phys. Chem. B, 106, 2520 (2002). |
| 38. | T. Sasaki, K. Ohno, Y. Nakazawa, Macromolecules, 35, 4317 (2002). |
| 39. | T. Sasaki, A. Katsuragi, O. Mochizuki, Y. Nakazawa, J. Phys. Chem. B, 107, 7659 (2003). |
| 40. | T. Sasaki, O. Mochizuki, K. Noborio, Y. Nakazawa, J. Phys. Chem. B, 108, 17083 (2004). |
| 41. | Y. Nakazawa, T. Sasaki, Chem. Lett., 33, 242 (2004). |
| 42. | T. Sasaki, O. Mochizuki, Y. Nakazawa, G. Fukunaga, T. Nakamura, K. Noborio, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 1329 (2004). |
| 43. | H. Ono, T. Kawamura, N. M. Frias, K. Kitamura, N. Kawatsuki, H. Norisada, Adv. Mater., 12, 143 (2000). |
| 44. | H. Ono, N. Kawatsuki, Opt. Lett., 22, 1144 (1997) |
| 45. | A. Golemme, B.L. Bolodin, B. Kippelen, N. Peyghambarian, Opt. Lett., 22, 1226 (1997) |
| 46. | H. Ono, N. Kawatsuki, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 36, 6444 (1997) |
| 47. | H. Ono, I. Sato, N. Kawatsuki, Appl. Phys. Lett., 72, 1942 (1998) |
| 48. | H. Ono, N. Kawatsuki, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 38, 737 (1999) |
| 49. | H. Ono, A. Hanazawa, T. Kawamura, H. Norisada, N. Kawatsuki, J. Appl. Phys., 86, 1785 (1999) |
| 50. | H. Ono, N. Kawatsuki, J. Appl. Phys., 85, 2482 (1999) |
| 51. | H. Ono,T. Kawamura, N. Kawatsuki, H. Norisada, T. Yamamoto, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 38, L1258 (1999) |
| 52. | H. Ono, N. Kawatsuki, J. Nonlinear Opt.Phys. Mater., 8, 329 (1999) |
| 53. | H. Ono, T. Kawamura, N.M. Frias, K. Kitamura, N. Kawatsuki, H. Norisada, T. Yamamoto, J. Appl. Phys., 88, 3853 (2000) |
| 54. | H. Ono, T. Kawamura, N.M. Frias, K. Kitamura, N. Kawatsuki, H. Norisada, Adv. Mater., 12, 143 (2000) |
| 55. | H. Ono, K. Kitamura, N. Kawatsuki, H. Norisada, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 40, 1328 (2001) |
| 56. | U. Hofmann, M. Grasruck, A. Leopold, A. Schreiber, S. Schloter, C. Hohle, P. Strohriegl, D. Haarer, S. J. Zilker, J. Phys. Chem. B, 104, 3887 (2000). |
| 57. | O. Ostroverkhova, W. E. Moerner, Appl. Phys. Lett., 82, 3602 (2003). |
photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative
photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative
photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative
photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative
photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative
photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative
photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative
photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative
photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative
photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative photorefrative
photorefrative photorefrative