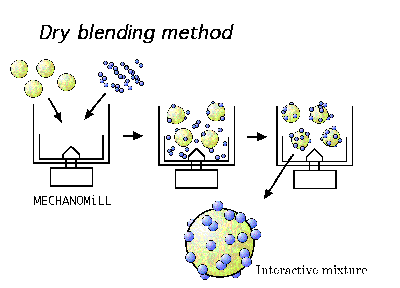

In the dry blending process using a binary cohesive-powder mixture which contains two different sizes, it is well known that finer particles adhere preferentially on the surface of the coarse particles. This type mixture has been called an interactive mixture.
The blending of fine and coarse particles breaks down the agglomerates of fine and coarse powders, and produces an electric charge by contact and collision between particles. Fine and coarse particles do not revert to the former agglomerates. The blending operation produces new agglomerates in which fine particles are adhered to the surface of the coarse particles. In the first step, however, the coating particles randomly adhere onto the surface of the core particles.